Find out how it works and how it will transform the way we communicate.
5G technology is starting to make headlines around the world, but not everyone understands what it is capable of or why we even need it. This next-generation wireless networking technology could transform the way people connect with one another and offer brand-new ways to communicate, ushering in a wave of new technologies in its wake.
There is also a great deal of misinformation about 5G available on the Internet. A quick search can lead you to wild conspiracy theories about its effect on pandemic resilience, as well as plausible-but-unproven speculations about the impact on the environment, and much more.
We’ve gathered and analyzed the most authoritative evidence available to set the record straight on 5G – what it is, how it works, and what drawbacks it presents.
What Is 5G, and Why Do We Need It?
5G is a next-generation wireless networking technology that promises faster speeds and lower energy consumption than the current 4G LTE standard.
5G networking offers the ability to reduce latency – the time it takes for mobile devices to make requests and get responses from servers – to near-zero. This, along with increased bandwidth, will overcome many of the difficulties that manufacturers face today, enabling new advances like self-driving cars and safer industrial machinery.
While there is always a demand for faster networking speed, the energy consumption difference is what many telecommunications professionals are most excited about. Healthcare companies are already designing implantable devices that can monitor patients’ vital signs and send clinical data directly to doctors from anywhere in the world. This is not possible with 4G technology – the battery for such a device would need to be recharged far too often.
How Does It Work?
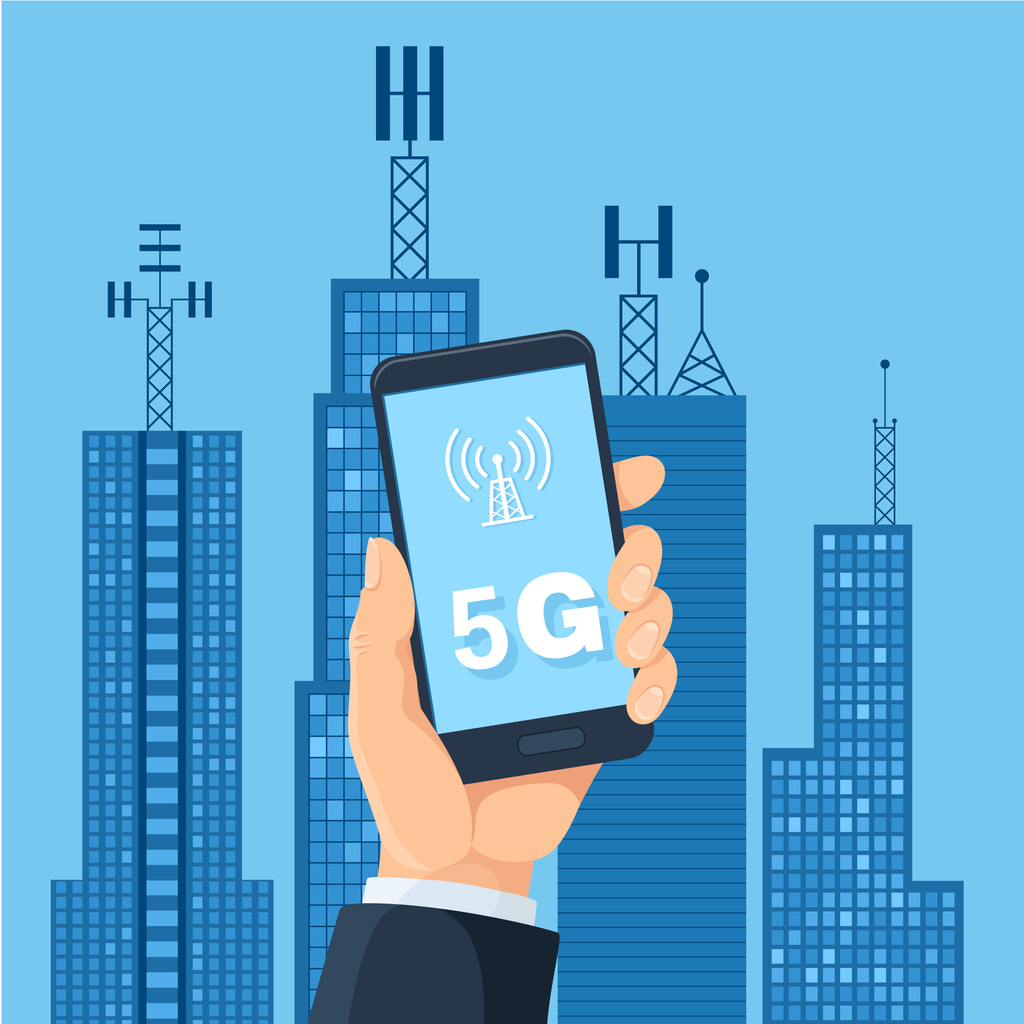

5G layers on top of existing low-band and mid-band networking infrastructure. While low-band airwaves travel great distances, they don’t offer a large number of channels, which limits their application. Mid-band airwaves include most current mobile and Wi-Fi frequencies, while high-band 5G operates on brand-new frequencies far above anything that has been used before.
Since high-band frequencies can’t travel the large distances that low-band frequencies can, telecommunications companies have to deploy a large number of short-range 5G base stations. These “small cell” antennas are roughly the size of a pizza box and carry data within a very short range. Telecommunications providers will deploy millions of these in the next few years.
Drawbacks to 5G: The Facts
Reputable medical professionals agree that 5G doesn’t represent a greater threat than any existing telecommunications infrastructure. 5G devices do emit electromagnetic radiation, but the power of every combined telecom device on the planet is nearly nothing compared to standing in the light of the sun for a few minutes.
Experts have reasonable concerns about 5G adoption, which may contribute to income inequality by concentrating on affluent communities and leaving most rural populations in the dark. Cybersecurity experts are also concerned about 5G security, especially when self-driving cars and healthcare monitoring devices become commonplace.
Get in touch with the SMB Solutions team for help improving your internet connectivity and devices.